Sky objects are pseudo-objects injected into the data processing pipeline using the SkyObjectsTask. Using coadded imaging, a number of randomly located sky objects per patch are placed such that their footprints do not overlap with any other detected object footprint. The maximum number of placed sky objects is currently set to 100 per patch, whilst the apparent size of each is currently set to an 8 pixel radius. These parameters are configurable using the nSources and sourceRadius configuration parameters, respectively.
Sky objects provide valuable QA data, allowing us to generate relevant sky statistics for subsequent analysis. Sky objects are generated on coadded imaging, and no equivalent has previously existed for single frame (visit-level) imaging. Following standard naming conventions, objects are detections on combined coadded imaging, whilst sources are detections at the single frame visit level.
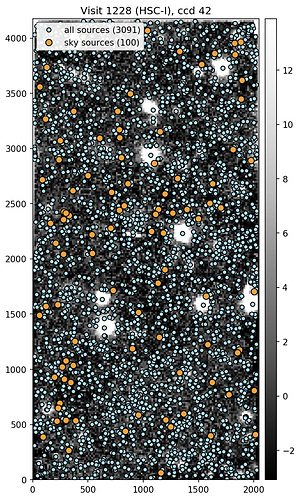
Ticket DM-23078 now adds sky sources to visit-level single frame processed imaging. Sky sources are implemented in exactly the same manner as sky objects, with up to nSources sky sources randomly placed for any given CCD. They may be selected (and excluded) from output catalogues using the sky_source flag.
An example image for Visit 1228 (HSC-I), CCD 42 is shown below. All detected sources are identified by small blue circles, whilst placed sky sources are represented by large orange circles. Note, the size of the circles are not to scale with the underlying sources. The underlying image is a calexp image, linearly scaled, and binned into 16x16 super-pixel blocks.